Waste management has long been viewed as a costly necessity, with industries paying significant sums to dispose of sludge generated from Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs) and Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs). However, modern advancements in sludge treatment technology are flipping this narrative. By investing in innovative machinery such as Sludge Paddle Dryers and Agitated Thin Film Dryers (ATFDs), industries can transform their sludge into a valuable resource, unlocking new streams of revenue. This article delves into how these technologies work, their benefits, and how they can help industries turn waste into profit.
—
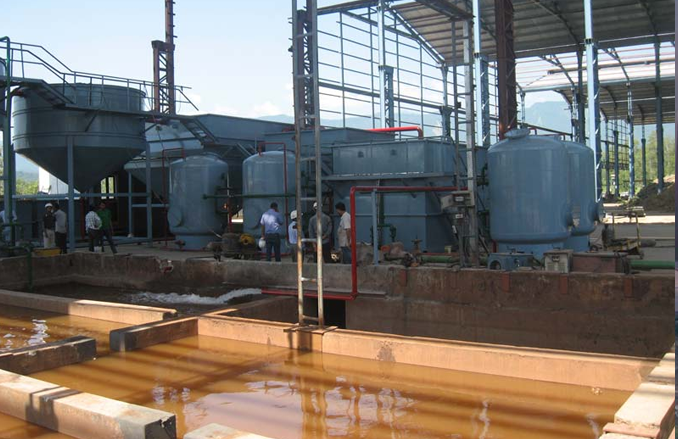
The Challenge: Managing ETP and STP Sludge
ETP and STP sludge are byproducts of wastewater treatment. Typically, this sludge is wet, bulky, and expensive to handle. Traditional disposal methods involve transporting the sludge to landfills or incinerators, which not only incur significant costs but also pose environmental risks. With tightening regulations on waste disposal and rising costs, industries are seeking sustainable alternatives.
This is where modern sludge management technologies step in, transforming what was once a liability into a valuable asset.
—
The Solution: Advanced Sludge Drying Technologies
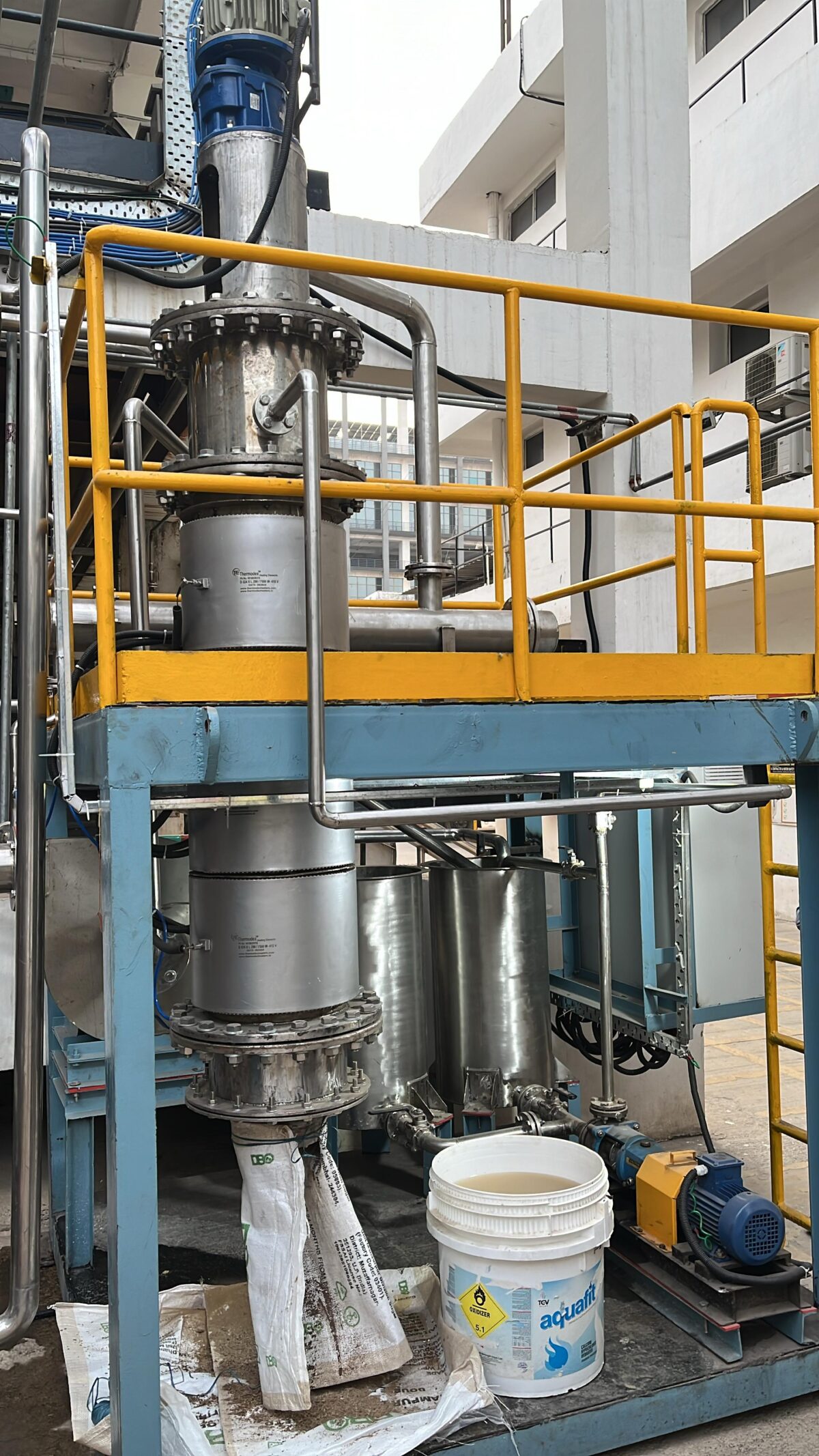
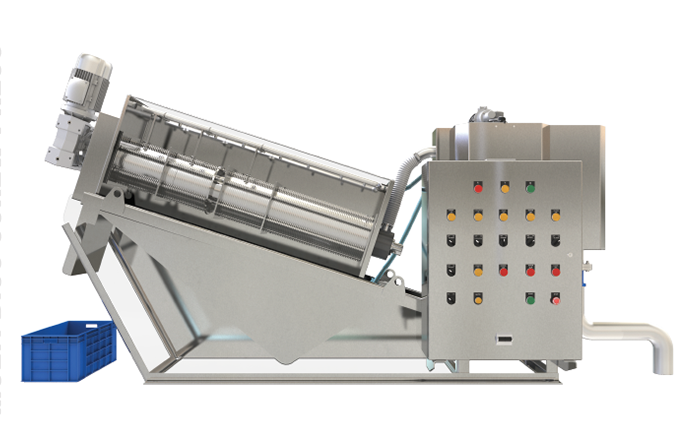
1. Sludge Paddle Dryer
The Sludge Paddle Dryer is a cutting-edge solution designed to efficiently dry wet sludge. It uses hollow paddles filled with a heating medium, such as steam or thermal oil, to transfer heat to the sludge. The continuous agitation of the paddles ensures uniform drying and prevents material from sticking to the surfaces.
– Key Benefits:
– Reduces sludge volume significantly by extracting moisture.
– Converts wet sludge into a dry, powdered form.
– Operates with low energy consumption and minimal maintenance.
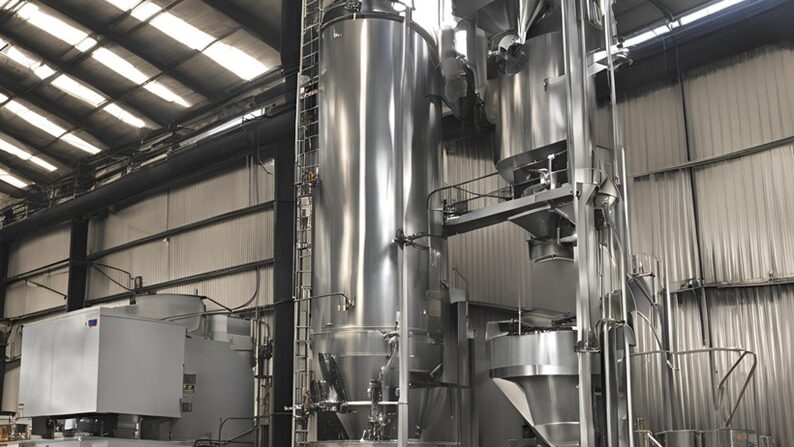
2. Agitated Thin Film Dryer (ATFD)
The Agitated Thin Film Dryer (ATFD) is another powerful technology for sludge treatment. It is specifically designed to handle high-viscosity materials, making it ideal for reducing sludge to a dry powder. In this system, sludge is spread into a thin film over a heated surface using rotating blades, allowing for rapid evaporation of moisture.
– Key Benefits:
– Handles even the most challenging sludge types with ease.
– Produces dry powder with consistent quality.
– Compact design and efficient operation.
—
Turning Sludge into Powdered Gold
Using these technologies, wet sludge from ETPs and STPs can be processed into a fine, dry powder. This transformation has several advantages:
1. Volume Reduction
Drying sludge reduces its weight and volume by up to 80-90%. This dramatically lowers transportation and storage costs.
2. Ease of Handling
The powdered form is easier to handle, transport, and store compared to wet sludge.
3. Marketability
The powdered sludge, depending on its characteristics, can be sold to various industries:
– Cement Industry: Used as an alternative raw material or fuel due to its organic content.
– Construction Industry: Incorporated into construction materials like bricks and tiles.
– Textile Industry: Certain sludge types can be reused in dyeing processes or as fillers.
– Other Applications: Potential uses include fertilizers, soil conditioners, and even energy generation.
By identifying the specific characteristics of your sludge, you can target industries that value it as a resource, effectively turning disposal costs into a new revenue stream.
—
Transforming the Waste Paradigm
The economic benefits of this approach are undeniable. Industries can eliminate the need to pay for sludge disposal and instead generate revenue by selling the dried product. This shift not only improves profitability but also enhances sustainability by reducing landfill dependency and promoting resource recovery.
—
Experience the Transformation Firsthand
With over 30 years of expertise and 2,000+ successful installations worldwide, we have been at the forefront of sludge treatment innovation. Our solutions, including Sludge Paddle Dryers and ATFDs, have helped countless industries achieve cost savings and environmental compliance.
If you’d like to see how this works, we invite you to visit one of our installations. Alternatively, we can conduct a trial at your site using our state-of-the-art pilot plants to demonstrate the potential of sludge drying for your operations.
—
Get in Touch
Curious to learn more about how you can turn your sludge into savings? Contact us today!
– Phone: +91-9646396191
– Email: [marketing@parashydrotech.com]
Follow us for more updates and insights:
– YouTube Channel
– LinkedIn Profile
Together, let’s redefine waste management and unlock the hidden value in your sludge.