Our Product
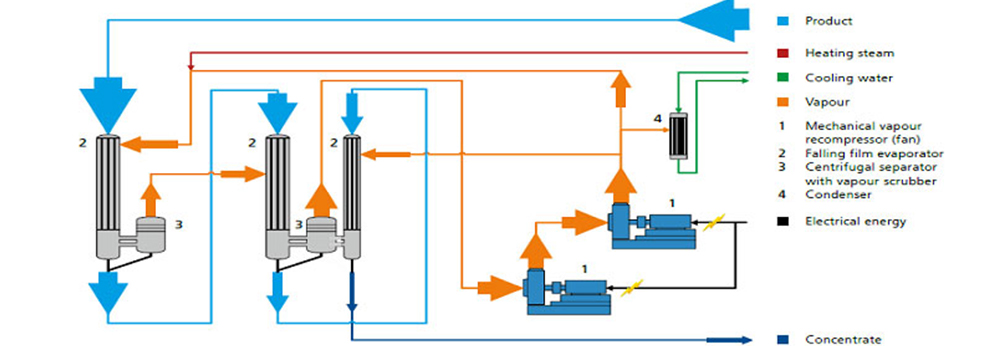
MVR
Mechanical Vapour Recompression-(MVRE)is the most efficient Evaporation Technique driven by electrical energy thus reduces operating cost of steam and cooling water required in the process.
<< Low Operating Cost System.
<< No Cooling Water Required.
<< No External Heat Source Required.
<< Low Specific Energy Consumption.

MVR Evaporators
Various evaporation techniques are used to concentrate fluids or to achieve Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) in wide-ranging industries including dairy, food, pharmaceutical, and chemical, textile, paper etc. Evaporating water from solution is an energy-intensive process. It is often one of the main contributors to a plant’s operating costs Over the past 10-15 years, Mechanical vapor recompression (MVRE) has become the preferred system in many industries, because of its economy and simplicity of operation. In most instances, the need for steam to provide heat for the evaporation and cooling water for condensing the overhead vapors is virtually eliminated; by installing MVRE. A wide range of turndown is possible in MVRE.
Principle of Operation
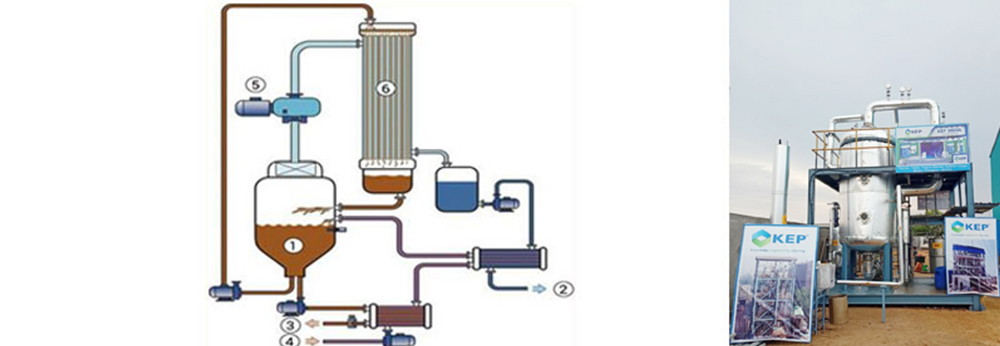
The preheated wastewater stream enters an evaporator chambers (6) from boiling chamber/separation tank (1) through Recirculation pump which is circulating heated waste water through the main heat exchanger (6) and back into the separation tank (1). Water vapor flows up through the mist pad to inlet side of MVR fan (5). Compressed steam from MVR fan (5) is forced through the steam side of main heat exchanger (6) giving up latent heat to the counter flowing wastewater.High temperature condensate flows out of the main heat exchanger (6). Concentrate (3) is periodically discharged based on temperature, conductivity or time from separation tank (1). Incoming wastewater (4) is preheated as it passes through a heat exchanger transferring heat from and cooling the exiting pure condensate (2) and concentrate (3) flows.